/* Soccer Scores - This program stores the following data about a soccer
player in a structure:
* Player's Name
* Player's Number
* Points Scored by Player
The program keeps an array of 12 of these structures. Each element is
for a different player on a team. When the program runs, it asks the
user to enter the data for each player. It then shows a table that lists
each player's number, name and points scored. The program calculates and
displays the total points earned by the team. The number and name of the
player who has earned the most points is also displayed.
Input Validation: No negative values for player's numbers or points scored
are accepted. */
#include "Utility.h"
struct TeamData
{
string playerName; /* Player's name */
int tricotNumber; /* Player's tricot number */
int pointsScored; /* Player's points */
};
struct SeasonData
{
string topPlayer; /* Top player's name */
int highscore; /* The highest score achieved by a player */
int totalPoints; /* Total points scored by the whole team */
int topPlayerNum; /* Top player's tricot number */
};
void initStructure(TeamData [], const int);
void getPlayerData(TeamData [], const int);
bool validateInput(TeamData [], const int);
void getTopPlayer(TeamData [], SeasonData &, const int);
void getTotalScore(TeamData [], SeasonData &, const int);
void displayTeamData(const TeamData [], const SeasonData &, const int);
int main()
{
const int NUM_PLAYERS = 12;
/* Array of structures */
TeamData team[NUM_PLAYERS];
/* SeasonData Structure */
SeasonData players = { "\0", 0, 0, 0 };
initStructure(team, NUM_PLAYERS);
getPlayerData(team, NUM_PLAYERS);
getTopPlayer(team, players, NUM_PLAYERS);
getTotalScore(team, players, NUM_PLAYERS);
displayTeamData(team, players, NUM_PLAYERS);
pauseSystem();
return 0;
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: initStructure
This function accepts an array of structures as parameter.
It initializes all members of the structure to default
values.
********************************************************** */
void initStructure(TeamData pData[], const int NUM_PLAYERS)
{
for (int index = 0; index < NUM_PLAYERS; index++)
{
pData[index].playerName = "\0";
pData[index].tricotNumber = 0;
pData[index].pointsScored = 0;
}
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: getPlayerData
This function accepts an array of structures as parameter.
The user is asked to enter data for twelve players of a
soccer team. This data is stored in the appropriate member
variables of the structure.
********************************************************** */
void getPlayerData(TeamData pData[], const int NUM_PLAYERS)
{
bool valid = false;
cout << "\n\tF.C. TOKYO - PLAYER STATISTICS\n\n";
for (int index = 0; index < NUM_PLAYERS; index++)
{
cout << "\n\tEnter the name of Player # "
<< (index + 1) << ": ";
getline(cin, pData[index].playerName);
cout << "\tEnter " << pData[index].playerName
<< "'s tricot number: ";
cin >> pData[index].tricotNumber;
valid = validateInput(pData, index);
cout << "\tEnter " << pData[index].playerName
<< "'s points scored: ";
cin >> pData[index].pointsScored;
valid = validateInput(pData, index);
cin.ignore();
}
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: validateInput
This function accepts an array of structures as argument.
It validates the input.
********************************************************** */
bool validateInput(TeamData pData[], const int index)
{
bool valid = false;
while (pData[index].tricotNumber < 0)
{
cout << "\n\tPlease enter a valid tricot number.\n\n"
<< "\tEnter " << pData[index].playerName
<< "'s tricot number: ";
cin >> pData[index].tricotNumber;
}
while (pData[index].pointsScored < 0)
{
cout << "\n\tPlease enter a valid score.\n\n"
<< "\tEnter " << pData[index].playerName
<< "'s points scored: ";
cin >> pData[index].pointsScored;
}
return valid;
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: getTopPlayer
This function accepts an array of structures, as well as a
structure reference variable as parameters. It determines
the highest score achieved by a player. The score, name
and tricot-number of this player is stored in the member
variables of the SeasonData structure.
********************************************************** */
void getTopPlayer(TeamData pData[], SeasonData &players,
const int NUM_PLAYERS)
{
players.highscore = pData[0].pointsScored;
for (int index = 0; index < NUM_PLAYERS; index++)
{
if (pData[index].pointsScored >= players.highscore)
{
players.highscore = pData[index].pointsScored;
players.topPlayer = pData[index].playerName;
players.topPlayerNum = pData[index].tricotNumber;
}
}
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: getTotalScore
This function accepts an array of structures, as well as a
structure reference variable as parameters. It calculates
and stores the total score achieved during the season.
********************************************************** */
void getTotalScore(TeamData pData[], SeasonData &players,
const int NUM_PLAYERS)
{
for (int index = 0; index < NUM_PLAYERS; index++)
{
players.totalPoints += pData[index].pointsScored;
}
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: displayData
This function accepts an array of structures, as well as a
structure reference variable as parameters. It displays:
* The player's names
* The player's numbers
* The player's scores
* The player's name who achieved the highest score
* The player's tricot-number
* The player's score
********************************************************** */
void displayTeamData(const TeamData pData[], const SeasonData &players,
const int NUM_PLAYERS)
{
cout << "\n\n\n\tF.C. TOKYO - SEASON RESULTS\n\n\n\t";
cout << setw(17) << left << "PLAYER NAME"
<< setw(13) << right << "PLAYER NUMBER"
<< setw(16) << right << "PLAYER SCORE" << "\n\t";
cout << setw(47) << setfill('-') << "\n" << setfill(' ');
for (int index = 0; index < NUM_PLAYERS; index++)
{
cout << "\t";
cout << setw(17) << left << pData[index].playerName
<< setw(13) << right << pData[index].tricotNumber
<< setw(12) << right << pData[index].pointsScored << " pts\n";
}
cout << "\t" << setw(47) << setfill('-')
<< "\n" << setfill(' ');
cout << "\tOverall Team Score " << setw(23) << right
<< players.totalPoints << " pts\n";
cout << "\n\n\tTOP PLAYER\n\t";
cout << setw(47) << setfill('-') << "\n" << setfill(' ') << "\t";
cout << setw(17) << left << players.topPlayer
<< setw(13) << right << players.topPlayerNum
<< setw(12) << right << players.highscore << " pts";
}
Saturday, May 27, 2017
Programming Challenge 11.6 - Soccer Scores
Bugfixes
While working on my current Programming Challenge, I noticed that something wasn't working as expected. The source of the problem was an if-statement to determine the highest score achieved by a player. Everything seemed to be working, except when player 1 has achieved the highest score.
The original if-statement:
if (pData[index].pointsScored > players.highscore)
The corrected if-statement:
if (pData[index].pointsScored >= players.highScore)
As it turns out, this is the same stupid mistake I made in both Programming Challenge 11.04 and Programming Challenge 11.05. The difference is that I didn't notice it right away. The reason for not noticing it was, that I never assigned JANUARY the lowest or highest amounts of rainfall to see whether it works.
if (metData[index].totalRainfall <= yearly.lowestPpt)
if (metData[index].totalRainfall >= yearly.highestPpt)
I fixed the relevant parts of code and updated the Blog-posts, so that everything should work flawlessly now. Sorry everyone!
Programming Challenge 11.5 - Weather Statistics Modification
/* Weather Statistics Modification - This is a modification of Programming
Challenge 11.04. It defines an enumerated data type with enumerators for
the months. The program uses the enumerated type to step through the
elements of the array. */
#include "Utility.h"
struct WeatherData
{
string monthNames; /* The month names */
double totalRainfall; /* The total amount of rainfall */
double highTemp; /* The highest measured temperature */
double lowTemp; /* The lowest measured temperature */
double avgTempMonths; /* The average monthly temperatures */
};
struct YearSummary
{
double totalPpt; /* Year total amount of precipitation */
double avgPpt; /* Average yearly precipitation */
double highestPpt; /* Highest amount of rainfall */
double lowestPpt; /* Lowest amount of rainfall */
string mNameHighest; /* Name of month with highest precipitation */
string mNameLowest; /* Name of month with lowest precipitation */
double avgTempYear; /* Average yearly temperature */
double avgHighTemp; /* Average yearly high temperature */
double avgLowTemp; /* Average yearly low temperature */
double highestTemp; /* Highest measured temperature */
double lowestTemp; /* Lowest measured temperature */
};
enum monthNames
{
JANUARY, FEBRUARY, MARCH, APRIL, MAY, JUNE, JULY,
AUGUST, SEPTEMBER, OCTOBER, NOVEMBER, DECEMBER
} mNames;
void getMetData(WeatherData [], int);
bool validateInput(WeatherData[], int);
void calcAvgTemps(WeatherData [], YearSummary &, int);
void calcPpt(WeatherData[], YearSummary &, int);
void getPptAmount(WeatherData[], YearSummary &, int);
void displayMetData(const WeatherData [], const YearSummary &, int);
int main()
{
const int MONTHS = 12;
/* Cast the first enumerator to int */
int mCount = static_cast<monthNames>(mNames);
/* Array of structures. The monthNames member is initialized. */
WeatherData metData[MONTHS] = { { "JANUARY" }, { "FEBRUARY" }, { "MARCH" },
{ "APRIL" }, { "MAY" }, { "JUNE" },
{ "JULY" }, { "AUGUST" }, { "SEPTEMBER" },
{ "OCTOBER" }, { "NOVEMBER" }, { "DECEMBER" } };
/* Structure variable definition, with all struct
members initialized to default values */
YearSummary yearly = { 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, "\0", "\0", 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 };
getMetData(metData, mCount);
calcAvgTemps(metData, yearly, mCount);
calcPpt(metData, yearly, mCount);
getPptAmount(metData, yearly, mCount);
displayMetData(metData, yearly, mCount);
pauseSystem();
return 0;
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: getMetData
This function uses an array of structs as parameter, to
get the following information from the user:
* The total amount of rainfall for each month
* The highest measured temperature
* The lowest measured temperature
This information is then stored in the appropriate member
variables.
********************************************************** */
void getMetData(WeatherData metData[], int mCount)
{
bool valid = false;
cout << "\n\tSTR Data Center - Data Entry System\n\n";
for (; mCount <= DECEMBER; mCount++)
{
cout << "\n\tEnter data for " << metData[mCount].monthNames << "\n";
cout << "\n";
cout << "\t" << setw(31) << right << setfill('±')
<< "\n" << setfill(' ');
cout << "\tTotal amount of rainfall" << setw(7) << right << ": ";
cin >> metData[mCount].totalRainfall;
valid = validateInput(metData, mCount);
cout << "\tHighest measured temperature" << setw(3) << right << ": ";
cin >> metData[mCount].highTemp;
valid = validateInput(metData, mCount);
cout << "\tLowest measured temperature" << setw(4) << right << ": ";
cin >> metData[mCount].lowTemp;
valid = validateInput(metData, mCount);
cout << "\t" << setw(31) << right << setfill('±')
<< "\n" << setfill(' ') << "\n";
}
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: validate Input
This function accepts an array of structures as parameter.
It validates the input.
********************************************************** */
bool validateInput(WeatherData metData[], int mCount)
{
bool valid = false;
while (metData[mCount].totalRainfall < 0)
{
cout << "\n\tInvalid input. The total amount of "
<< " rainfall can't be lower than 0.\n\n";
cout << "\tTotal amount of rainfall" << setw(7) << right << ": ";
cin >> metData[mCount].totalRainfall;
}
while (metData[mCount].highTemp < -100 ||
metData[mCount].highTemp > 140)
{
cout << "\n\tTemperatures above +140F or below -100F "
<< "are not accepted\n\n";
cout << "\tHighest measured temperature" << setw(3) << right << ": ";
cin >> metData[mCount].highTemp;
}
while (metData[mCount].lowTemp < -100 ||
metData[mCount].lowTemp > 140)
{
cout << "\n\tTemperatures below -100F or above +140F are "
<< "not accepted.\n\n";
cout << "\tLowest measured temperature" << setw(3) << right << ": ";
cin >> metData[mCount].lowTemp;
}
return valid;
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: calcAvgTemps
This function uses an array of structs and a YearSummary
reference variable, to calculate:
* The monthly average temperatures
* The yearly total average temperature of all average
temperatures (Are you confuzzled now? ;-))
* The highest average temperature
* The lowest average temperature
The results are stored in the appropriate struct members.
********************************************************** */
void calcAvgTemps(WeatherData metData[], YearSummary &yearly, int mCount)
{
for (; mCount <= DECEMBER; mCount++)
{
/* Calculates the monthly average temperatures */
metData[mCount].avgTempMonths = (metData[mCount].highTemp +
metData[mCount].lowTemp) / 2;
yearly.avgTempYear += metData[mCount].lowTemp +
metData[mCount].highTemp;
yearly.avgHighTemp += metData[mCount].highTemp / 12;
yearly.avgLowTemp += metData[mCount].lowTemp / 12;
}
yearly.avgTempYear /= 24;
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: calcPpt
This function uses an array of structs and a YearSummary
reference variable, to calculate the total and average
precipitation amounts for the whole year.
********************************************************** */
void calcPpt(WeatherData metData[], YearSummary &yearly, int mCount)
{
for (; mCount <= DECEMBER; mCount++)
{
yearly.totalPpt += metData[mCount].totalRainfall;
yearly.avgPpt = yearly.totalPpt / 12;
}
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: getPptAmount
This function uses an array of structs and a YearSummary
reference variable, to determine the month with the lowest
and highest amounts of rainfall. The month names and the
amounts of precipitation are stored in their appropriate
member variables.
********************************************************** */
void getPptAmount(WeatherData metData[], YearSummary &yearly, int mCount)
{
yearly.highestPpt = metData[0].totalRainfall;
yearly.lowestPpt = metData[0].totalRainfall;
for (; mCount <= DECEMBER; mCount++)
{
if (metData[mCount].totalRainfall <= yearly.lowestPpt)
{
yearly.lowestPpt = metData[mCount].totalRainfall;
yearly.mNameLowest = metData[mCount].monthNames;
}
if (metData[mCount].totalRainfall >= yearly.highestPpt)
{
yearly.highestPpt = metData[mCount].totalRainfall;
yearly.mNameHighest = metData[mCount].monthNames;
}
}
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: displayMetData
This function uses an array of structs and a const
reference parameter to display their contents.
********************************************************** */
void displayMetData(const WeatherData metData[], const YearSummary &yearly,
int mCount)
{
cout << "\n\n\tSTR Data Center - Weather Statistic Summary 2016\n\n\n\n\t";
cout << setw(9) << left << "MONTH NAME"
<< setw(19) << right << "Rainfall Amount"
<< setw(20) << right << "Highest Temp"
<< setw(20) << right << "Lowest Temp"
<< setw(20) << right << "Average Temp" << "\n";
cout << "\t" << setw(90) << right << setfill('±')
<< "\n" << setfill(' ');
cout << fixed << showpoint << setprecision(2);
for (; mCount <= DECEMBER; mCount++)
{
cout << "\t" << setw(9) << left << metData[mCount].monthNames
<< setw(20) << right << metData[mCount].totalRainfall
<< setw(20) << right << metData[mCount].highTemp
<< setw(20) << right << metData[mCount].lowTemp
<< setw(20) << right << metData[mCount].avgTempMonths << "\n";
}
cout << "\t" << setw(90) << right << setfill('±')
<< "\n" << setfill(' ');
cout << "\n\n\tSTR Data Center - Additional Weather Statistic "
"Information\n\n";
cout << "\tThe total amount of rainfall was: "
<< setw(25) << right << yearly.totalPpt << " mm"
<< "\n\tThe average amount of rainfall was: "
<< setw(23) << right << yearly.avgPpt << " mm"
<< "\n\n\tThe month with the highest amount of rainfall was: "
<< setw(10) << right << yearly.mNameHighest
<< "\n\tThe highest measured amount of rainfall was: "
<< setw(13) << right << yearly.highestPpt << " mm"
<< "\n\n\tThe month with the lowest amount of rainfall was: "
<< setw(11) << right << yearly.mNameLowest
<< "\n\tThe lowest measured amount of rainfall was: "
<< setw(15) << right << yearly.lowestPpt << " mm" << "\n";
cout << "\n\tThe average of all monthly average temperatures was: "
<< setw(6) << right << yearly.avgTempYear << " F"
<< "\n\tThe highest average yearly temperature was: "
<< setw(15) << right << yearly.avgHighTemp << " F"
<< "\n\tThe lowest average yearly temperature was: "
<< setw(16) << right << yearly.avgLowTemp << " F" << "\n";
}
Example Output:
Thursday, May 25, 2017
Programming Challenge 11.4 - Weather Statistics
/* Weather Statistics - This program uses a structure to store the following
weather data for a particular month:
* Total Rainfall
* High Temperature
* Low Temperature
* Average Temperature
The program has an array of 12 structures to hold weather data for an
entire year. When the program runs, the user is asked to enter data for
each month. (The average temperature is calculated.) Once the data are
entered for all the months, the program calculates and displays the
average monthly rainfall, the total rainfall for the year, the highest
and lowest temperatures for the year (and the months they occurred in),
and the average of all the monthly average temperatures.
Input Validation: Only temperatures within the range between -100 and
+140 degrees Fahrenheit are accepted. */
#include "Utility.h"
struct WeatherData
{
string monthNames; /* The month names */
double totalRainfall; /* The total amount of rainfall */
double highTemp; /* The highest measured temperature */
double lowTemp; /* The lowest measured temperature */
double avgTempMonths; /* The average monthly temperatures */
};
struct YearSummary
{
double totalPpt; /* Year total amount of precipitation */
double avgPpt; /* Average yearly precipitation */
double highestPpt; /* Highest amount of rainfall */
double lowestPpt; /* Lowest amount of rainfall */
string mNameHighest; /* Name of month with highest precipitation */
string mNameLowest; /* Name of month with lowest precipitation */
double avgTempYear; /* Average yearly temperature */
double avgHighTemp; /* Average yearly high temperature */
double avgLowTemp; /* Average yearly low temperature */
double highestTemp; /* Highest measured temperature */
double lowestTemp; /* Lowest measured temperature */
};
void getMetData(WeatherData [], const int);
void calcAvgTemps(WeatherData [], YearSummary &, const int);
void calcPpt(WeatherData[], YearSummary &, const int);
void getPptAmount(WeatherData[], YearSummary &, const int);
void displayMetData(const WeatherData [], const YearSummary &, const int);
int main()
{
const int MONTHS = 12;
/* Array of structures. The monthNames member is initialized. */
WeatherData metData[MONTHS] = { { "JANUARY" }, { "FEBRUARY" }, { "MARCH" },
{ "APRIL" }, { "MAY" }, { "JUNE" },
{ "JULY" }, { "AUGUST" }, { "SEPTEMBER" },
{ "OCTOBER" }, { "NOVEMBER" }, { "DECEMBER" } };
/* Structure variable definition, with all struct
members initialized to default values */
YearSummary yearly = { 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, "\0", "\0", 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 };
getMetData(metData, MONTHS);
calcAvgTemps(metData, yearly, MONTHS);
calcPpt(metData, yearly, MONTHS);
getPptAmount(metData, yearly, MONTHS);
displayMetData(metData, yearly, MONTHS);
pauseSystem();
return 0;
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: getMetData
This function uses an array of structs as parameter, to
get the following information from the user:
* The total amount of rainfall for each month
* The highest measured temperature
* The lowest measured temperature
This information is then stored in the appropriate member
variables.
********************************************************** */
void getMetData(WeatherData metData[], const int MONTHS)
{
cout << "\n\tSTR Data Center - Data Entry System\n\n";
for (int count = 0; count < MONTHS; count++)
{
cout << "\n\tEnter data for " << metData[count].monthNames << "\n";
cout << "\t" << setw(31) << right << setfill('±')
<< "\n" << setfill(' ');
cout << "\tTotal amount of rainfall" << setw(7) << right << ": ";
cin >> metData[count].totalRainfall;
while (metData[count].totalRainfall < 0)
{
cout << "\tInvalid input. The total amount of rainfall can't be "
<< "lower than 0.\n";
cout << "\tTotal amount of rainfall" << setw(7) << right << ": ";
cin >> metData[count].totalRainfall;
}
cout << "\tHighest measured temperature" << setw(3) << right << ": ";
cin >> metData[count].highTemp;
while (metData[count].highTemp < -100 || metData[count].highTemp > 140)
{
cout << "\n\tTemperatures above +140F or below -100F "
<< "are not accepted\n\n";
cout << "\tHighest measured temperature" << setw(3) << right << ": ";
cin >> metData[count].highTemp;
}
cout << "\tLowest measured temperature" << setw(4) << right << ": ";
cin >> metData[count].lowTemp;
while (metData[count].lowTemp < -100 || metData[count].lowTemp > 140)
{
cout << "\n\tTemperatures below -100F or above +140F are "
<< "not accepted.\n\n";
cout << "\tLowest measured temperature" << setw(3) << right << ": ";
cin >> metData[count].lowTemp;
}
cout << "\t" << setw(31) << right << setfill('±')
<< "\n" << setfill(' ') << "\n";
}
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: calcAvgTemps
This function uses an array of structs and a YearSummary
reference variable, to calculate:
* The monthly average temperatures
* The yearly total average temperature of all average
temperatures (Are you confuzzled now? ;-))
* The highest average temperature
* The lowest average temperature
The results are stored in the appropriate struct members.
********************************************************** */
void calcAvgTemps(WeatherData metData[], YearSummary &yearly, const int MONTHS)
{
for (int index = 0; index < MONTHS; index++)
{
/* Calculates the monthly average temperatures */
metData[index].avgTempMonths = (metData[index].highTemp +
metData[index].lowTemp) / 2;
yearly.avgTempYear += metData[index].lowTemp +
metData[index].highTemp;
yearly.avgHighTemp += metData[index].highTemp / 12;
yearly.avgLowTemp += metData[index].lowTemp / 12;
}
yearly.avgTempYear /= 24;
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: calcPpt
This function uses an array of structs and a YearSummary
reference variable, to calculate the total and average
precipitation amounts for the whole year.
********************************************************** */
void calcPpt(WeatherData metData[], YearSummary &yearly, const int MONTHS)
{
for (int index = 0; index < MONTHS; index++)
{
yearly.totalPpt += metData[index].totalRainfall;
yearly.avgPpt = yearly.totalPpt / 12;
}
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: getPptAmount
This function uses an array of structs and a YearSummary
reference variable, to determine the month with the lowest
and highest amounts of rainfall. The month names and the
amounts of precipitation are stored in their appropriate
member variables.
********************************************************** */
void getPptAmount(WeatherData metData[], YearSummary &yearly, const int MONTHS)
{
yearly.highestPpt = metData[0].totalRainfall;
yearly.lowestPpt = metData[0].totalRainfall;
for (int index = 0; index < MONTHS; index++)
{
if (metData[index].totalRainfall <= yearly.lowestPpt)
{
yearly.lowestPpt = metData[index].totalRainfall;
yearly.mNameLowest = metData[index].monthNames;
}
if (metData[index].totalRainfall >= yearly.highestPpt)
{
yearly.highestPpt = metData[index].totalRainfall;
yearly.mNameHighest = metData[index].monthNames;
}
}
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: displayMetData
This function uses an array of structs and a const
reference parameter to display their contents.
********************************************************** */
void displayMetData(const WeatherData metData[], const YearSummary &yearly,
const int MONTHS)
{
cout << "\n\n\tSTR Data Center - Weather Statistic Summary 2016\n\n\n\n\t";
cout << setw(9) << left << "MONTH NAME"
<< setw(19) << right << "Rainfall Amount"
<< setw(20) << right << "Highest Temp"
<< setw(20) << right << "Lowest Temp"
<< setw(20) << right << "Average Temp" << "\n";
cout << "\t" << setw(90) << right << setfill('±')
<< "\n" << setfill(' ');
cout << fixed << showpoint << setprecision(2);
for (int count = 0; count < MONTHS; count++)
{
cout << "\t" << setw(9) << left << metData[count].monthNames
<< setw(20) << right << metData[count].totalRainfall
<< setw(20) << right << metData[count].highTemp
<< setw(20) << right << metData[count].lowTemp
<< setw(20) << right << metData[count].avgTempMonths << "\n";
}
cout << "\t" << setw(90) << right << setfill('±')
<< "\n" << setfill(' ');
cout << "\n\n\tSTR Data Center - Additional Weather Statistic "
"Information\n\n";
cout << "\tThe total amount of rainfall was: "
<< setw(25) << right << yearly.totalPpt << " mm"
<< "\n\tThe average amount of rainfall was: "
<< setw(23) << right << yearly.avgPpt << " mm"
<< "\n\n\tThe month with the highest amount of rainfall was: "
<< setw(10) << right << yearly.mNameHighest
<< "\n\tThe highest measured amount of rainfall was: "
<< setw(13) << right << yearly.highestPpt << " mm"
<< "\n\n\tThe month with the lowest amount of rainfall was: "
<< setw(11) << right << yearly.mNameLowest
<< "\n\tThe lowest measured amount of rainfall was: "
<< setw(15) << right << yearly.lowestPpt << " mm" << "\n";
cout << "\n\tThe average of all monthly average temperatures was: "
<< setw(6) << right << yearly.avgTempYear << " F"
<< "\n\tThe highest average yearly temperature was: "
<< setw(15) << right << yearly.avgHighTemp << " F"
<< "\n\tThe lowest average yearly temperature was: "
<< setw(16) << right << yearly.avgLowTemp << " F" << "\n";
}
Example Output:
Wednesday, May 24, 2017
Programming Challenge 11.3 - Corporate Sales Data
/* Corporate Sales Data - This program uses a structure to store the
following data on a company division:
* Division Name (such as East, West, North, or South)
* First-Quarter Sales
* Second-Quarter Sales
* Third-Quarter Sales
* Fourth-Quarter Sales
* Total Annual Sales
* Average Quarterly Sales
The program uses four variables of this structure. Each variable
represents one of the following corporate divisions: East, West,
North, and South. The user is asked for the four quarters' sales
figures for each division. Each division's total and average sales
are calculated and stored in the appropriate member of each structure
variable. These figures are then displayed on the screen.
Input Validation: No negative numbers for any sales figures are
accepted. */
#include "Utility.h"
struct SalesData
{
string divisionName; /* The division names */
double quarters[4]; /* Array for quaterly sales */
double total; /* Sales total */
double avgQtr; /* The average quarterly sales */
};
void getSalesData(SalesData [], const int);
void getSalesResult(SalesData [], const int);
void displaySalesData(const SalesData [], const int);
int main()
{
const int NUM_BRANCHES = 4; /* Number of branches */
/* Array of structures initialized with names,
assigned to the 'divisionName' structure member. */
SalesData divisions[NUM_BRANCHES] = { { "NORTH BRANCH" },
{ "SOUTH BRANCH" },
{ "EAST BRANCH" },
{ "WEST BRANCH" } };
getSalesData(divisions, NUM_BRANCHES);
getSalesResult(divisions, NUM_BRANCHES);
displaySalesData(divisions, NUM_BRANCHES);
pauseSystem();
return 0;
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: getSalesData
This function accepts a pointer to an array of structures
as argument. It asks for the sales data for each quarter,
for each of the four branches, North, South, East, and
West. The data is stored in the structure member.
********************************************************** */
void getSalesData(SalesData divisions[], const int NUM_BRANCHES)
{
int qtrs = 0;
int index = 0;
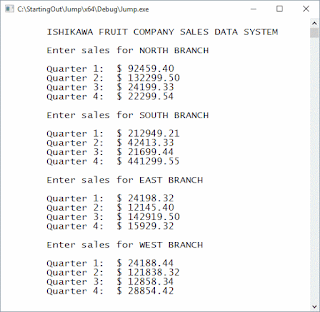
cout << "\n\tISHIKAWA FRUIT COMPANY SALES DATA SYSTEM\n";
for (index = 0; index < NUM_BRANCHES; index++)
{
cout << "\n\tEnter sales for "
<< divisions[index].divisionName << "\n\n";
for (qtrs = 0; qtrs < NUM_BRANCHES; qtrs++)
{
cout << "\tQuarter " << (qtrs + 1) << ": $ ";
cin >> divisions[index].quarters[qtrs];
/* The input is validated in this loop */
while (divisions[index].quarters[qtrs] <= 0.0)
{
cout << "\n\tInvalid input: The sales amount must be "
<< "positive.\n"
<< "\tPlease repeat your input.\n\n"
<< "\tQuarter " << (qtrs + 1) << ": $ ";
cin >> divisions[index].quarters[qtrs];
}
}
}
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: getSalesResult
This function uses two structure variables as parameters.
It calculates the sales total and average quaterly sales
for each of the four branches. The results are stored in
the members of each structure variable.
********************************************************** */
void getSalesResult(SalesData divisions[], const int NUM_BRANCHES)
{
int index = 0;
int qtrs = 0;
for (index = 0; index < NUM_BRANCHES; index++)
{
for (qtrs = 0; qtrs < 4; qtrs++)
{
/* Calculate the sales total*/
divisions[index].total += divisions[index].quarters[qtrs];
}
/* Calculate the quarterly average sales */
divisions[index].avgQtr = divisions[index].total / 4.0;
}
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: displayData
This function accepts an array of structs as argument. It
displays the sales total and quarterly average achieved by
each of the four branches.
********************************************************** */
void displaySalesData(const SalesData division[], const int NUM_BRANCHES)
{
cout << "\n\n\n\tISHIKAWA FRUIT COMPANY ANNUAL SALES REPORT\n\n";
for (int index = 0; index < NUM_BRANCHES; index++)
{
cout << fixed << showpoint << setprecision(2) << "\n\t";
cout << division[index].divisionName
<< "\n\n\tSales Total:" << setw(9) << "$ "
<< division[index].total << setw(25) << right
<< "\n\tQuarterly Average:" << setw(2) << "$"
<< setw(10) << right
<< division[index].avgQtr << "\n";
}
}
Example Output:
Tuesday, May 23, 2017
Programming Challenge 11.2 - Movie Profit
/* Movie Profit - This is a modification of the Movie Data program written
for Programming Challenge 11.01. This program uses a structure named
MovieData to store the following information about a movie:
* Title
* Director
* Year Released
* Running Time (in minutes)
* Production cost
* First year's profit or loss
The function that displays the movie data is modified so that it displays
the title, director, release year, running time, and first year's profit
or loss. */
#include "Utility.h"
struct MovieData
{
string title; /* The movie's title */
string director; /* The movie director's name */
int releaseYear; /* The year the movie was released */
int runningTime; /* The movie length in minutes */
double productionCost; /* The movie's production cost */
double revenue; /* The movie's first year profit or loss */
};
void getMovieData(MovieData &);
double getProfit(const MovieData &);
void repeatInput(MovieData &, double);
string formatOutput(const double);
void showMovieData(const MovieData &, const double);
int main()
{
/* Structure variable definitions */
MovieData movieOne;
MovieData movieTwo;
double profitM1 = 0.0; /* Holds the profit or loss of movie one */
double profitM2 = 0.0; /* Holds the profit or loss of movie two */
cout << "\n\tFavorite Movie Database\n\n";
getMovieData(movieOne);
profitM1 = getProfit(movieOne);
repeatInput(movieOne, profitM1);
getMovieData(movieTwo);
profitM2 = getProfit(movieTwo);
repeatInput(movieTwo, profitM2);
cout << "\n\tThese movies are now stored in your database:\n";
showMovieData(movieOne, profitM1);
showMovieData(movieTwo, profitM2);
pauseSystem();
return 0;
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: repeatInput
This function uses a structure reference variable as its
argument. It asks the user to confirm his or her input. If
the displayed information is incorrect, the user is asked
to repeat the input. If the user finds that the input is
correct, a message is displayed, telling the user that the
movie info has been added.
********************************************************** */
void repeatInput(MovieData &movieInfo, double profit)
{
char again = ' '; /* Holds the user's choice */
do
{
showMovieData(movieInfo, profit);
cout << "\tIs the data you entered correct? (Y/N): ";
cin >> again;
cin.ignore();
if (toupper(again) == 'Y')
{
cout << "\n\tThe following movie info has been added:\n";
showMovieData(movieInfo, profit);
}
else
{
cout << "\n\n\tPlease repeat your input:\n";
getMovieData(movieInfo);
profit = getProfit(movieInfo);
}
} while (toupper(again) == 'N' || toupper(again) != 'Y');
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: getMovieData
This function uses a structure reference variable as its
argument. It asks the user for data about his or her two
favorite movies. This data is stored in the structure.
********************************************************** */
void getMovieData(MovieData &movieInfo)
{
cout << "\n\tEnter the name of your favorite movie: ";
getline(cin, movieInfo.title);
cout << "\tEnter the name of the movie's director: ";
getline(cin, movieInfo.director);
cout << "\tEnter the year the movie was released: ";
cin >> movieInfo.releaseYear;
cout << "\tEnter the running time (in minutes): ";
cin >> movieInfo.runningTime;
cout << "\tEnter the movie's production cost: $";
cin >> movieInfo.productionCost;
cout << "\tEnter the movie's first-year revenue: $";
cin >> movieInfo.revenue;
cin.ignore();
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: getProfit
This function accepts a constant reference to a structure
variable as argument. It calculates the profit or loss of
the movies. The result of this calculation is returned.
********************************************************** */
double getProfit(const MovieData &movieInfo)
{
double total = 0.0; /* Holds the total profit or loss */
return total = movieInfo.revenue - movieInfo.productionCost;
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: showMovieData
This function accepts a constant reference to a structure
variable as argument. It displays the movie data.
********************************************************** */
void showMovieData(const MovieData &mData, const double profit)
{
string revenue; /* Holds the formatted profit */
cout << "\n\tMovie Title: " << mData.title << "\n"
<< "\tDirector: " << mData.director << "\n"
<< "\tRelease Year: " << mData.releaseYear << "\n"
<< "\tRunning Time: " << mData.runningTime << " minutes\n";
revenue = formatOutput(profit);
profit > 0 ? cout << "\n\tFirst-Year Profit: $" << revenue << "\n\n" :
cout << "\n\tFirst-Year Loss: $" << revenue << "\n\n";
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: showMovieData
This function formats the profit to make it more legible.
To achieve this, commata are inserted in the string object
holding the profit. Amounts between one-thousand, up to
nine-billion, are considered. Example:
* 1985456 becomes 1,985,456
* -92482948 becomes 92,482,948
If the string object contains a negative amount, the minus
sign is erased, before formatting takes place. The string
object is returned.
********************************************************** */
string formatOutput(const double profit)
{
string revenue = to_string((int)profit);
if (revenue.at(0) == '-')
{
revenue.erase(0,1);
}
/* This chained ternary operator determines the length of the
string object's contents. Based on the result, commata are
inserted at the appropriate substring position(s). */
revenue.length() == 4 ? revenue.insert(1, ",") :
revenue.length() == 5 ? revenue.insert(2, ",") :
revenue.length() == 6 ? revenue.insert(3, ",") :
revenue.length() == 7 ? revenue.insert(1, ","), revenue.insert(5, ",") :
revenue.length() == 8 ? revenue.insert(2, ","), revenue.insert(6, ",") :
revenue.length() == 9 ? revenue.insert(3, ","), revenue.insert(7, ",") :
revenue.length() == 10 ? revenue.insert(1, ","), revenue.insert(5, ","),
revenue.insert(9, ",") : revenue;
return revenue;
}
Example Output:
Monday, May 22, 2017
Programming Challenge 11.1 - Movie Data
/* Movie Data - This program uses a structure named MovieData to store the
following information about a movie:
* Title
* Director
* Year Released
* Running Time (in minutes)
The program creates two MovieData variables, stores values in their
members, and pass each one, in turn, to a function that displays the
information about the movie in a clearly formatted manner. */
#include "Utility.h"
struct MovieData
{
string title; /* The movie's title */
string director; /* The movie director's name */
int releaseYear; /* The year the movie was released */
int runningTime; /* The movie length in minutes */
};
void getMovieData(MovieData &);
void repeatInput(MovieData &);
void showMovieData(const MovieData &);
int main()
{
/* Structure variable definitions */
MovieData movieOne;
MovieData movieTwo;
cout << "\n\tFavorite Movie Database\n\n";
getMovieData(movieOne);
repeatInput(movieOne);
getMovieData(movieTwo);
repeatInput(movieTwo);
cout << "\n\tThese movies are now stored in your database:\n";
showMovieData(movieOne);
showMovieData(movieTwo);
pauseSystem();
return 0;
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: repeatInput
This function uses a structure reference variable as its
argument. It asks the user to confirm his or her input. If
the displayed information is incorrect, the user is asked
to repeat the input. If the user finds that the input is
correct, a message is displayed, telling the user that the
movie info has been added.
********************************************************** */
void repeatInput(MovieData &movieInfo)
{
char again = ' ';
do
{
showMovieData(movieInfo);
cout << "\tIs the data you entered correct? (Y/N): ";
cin >> again;
cin.ignore();
if (toupper(again) == 'Y')
{
cout << "\n\tThe following movie info has been added:\n";
showMovieData(movieInfo);
}
else
{
cout << "\n\n\tPlease repeat your input:\n";
getMovieData(movieInfo);
}
} while (toupper(again) == 'N' || toupper(again) != 'Y');
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: getMovieData
This function uses a structure reference variable as its
argument. It asks the user for data about his or her two
favorite movies. This data is stored in the structure.
********************************************************** */
void getMovieData(MovieData &movieInfo)
{
cout << "\n\tEnter the name of your favorite movie: ";
getline(cin, movieInfo.title);
cout << "\tEnter the name of the movie's director: ";
getline(cin, movieInfo.director);
cout << "\tEnter the year the movie was released: ";
cin >> movieInfo.releaseYear;
cout << "\tEnter the running time (in minutes): ";
cin >> movieInfo.runningTime;
cin.ignore();
}
/* **********************************************************
Definition: showMovieData
This function accepts a constant reference to a structure
variable as argument. It displays the movie data.
********************************************************** */
void showMovieData(const MovieData &mData)
{
cout << "\n\tMovie Title: " << mData.title << "\n"
<< "\tDirector: " << mData.director << "\n"
<< "\tRelease Year: " << mData.releaseYear << "\n"
<< "\tRunning Time: " << mData.runningTime << " minutes\n\n";
}
Example Output:
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)